Throughout human history, there have been pivotal moments when transformative ideas, inventions, or phenomena have reshaped the world in ways previously unimaginable. These eras are characterized by monumental shifts that redefine how we live, work, and think. One such moment was the Industrial Revolution, and today, we find ourselves on the cusp of another: the Intellectual Revolution, driven by artificial intelligence (AI).
Today, we stand at the dawn of the Intellectual Revolution, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence. While the Industrial Revolution transformed physical labor, the Intellectual Revolution is poised to reshape cognitive work.
A Look Back: The Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, which began in the late 18th century, marked a seismic shift in human history. For thousands of years, agriculture had been the dominant way of life. People lived off the land, and communities were largely self-sufficient. However, the invention of machinery, combined with the power of steam and later electricity, transformed society. Factories emerged, enabling mass production. Cities grew as people moved from rural areas in search of work. Economies became global as goods could be produced faster and traded widely.

Despite its many benefits, the Industrial Revolution was met with fear and resistance. One of the most common concerns was the loss of jobs. Automation threatened traditional crafts and manual labor, sparking protests such as the famous Luddite movement. These fears, however, eventually gave way to new opportunities. While some jobs disappeared, others were created, such as factory workers, engineers, and mechanics. Over time, society adapted, and the Industrial Revolution came to be seen as a period of unprecedented growth and innovation.
AI: The Catalyst of the Intellectual Revolution
Today, we stand at the dawn of the Intellectual Revolution, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence. While the Industrial Revolution transformed physical labor, the Intellectual Revolution is poised to reshape cognitive work. AI systems can now perform tasks that were once the exclusive domain of human intellect: composing music, diagnosing medical conditions, analyzing legal documents, and even generating complex code.
Unlike the machines of the Industrial Revolution, which required human operators, AI systems can function independently and, in some cases, outperform humans. This has led to both awe and apprehension. The primary concern is that AI’s ability to “think” and “learn” will render human knowledge and skills obsolete.
Intellectual Anxiety:
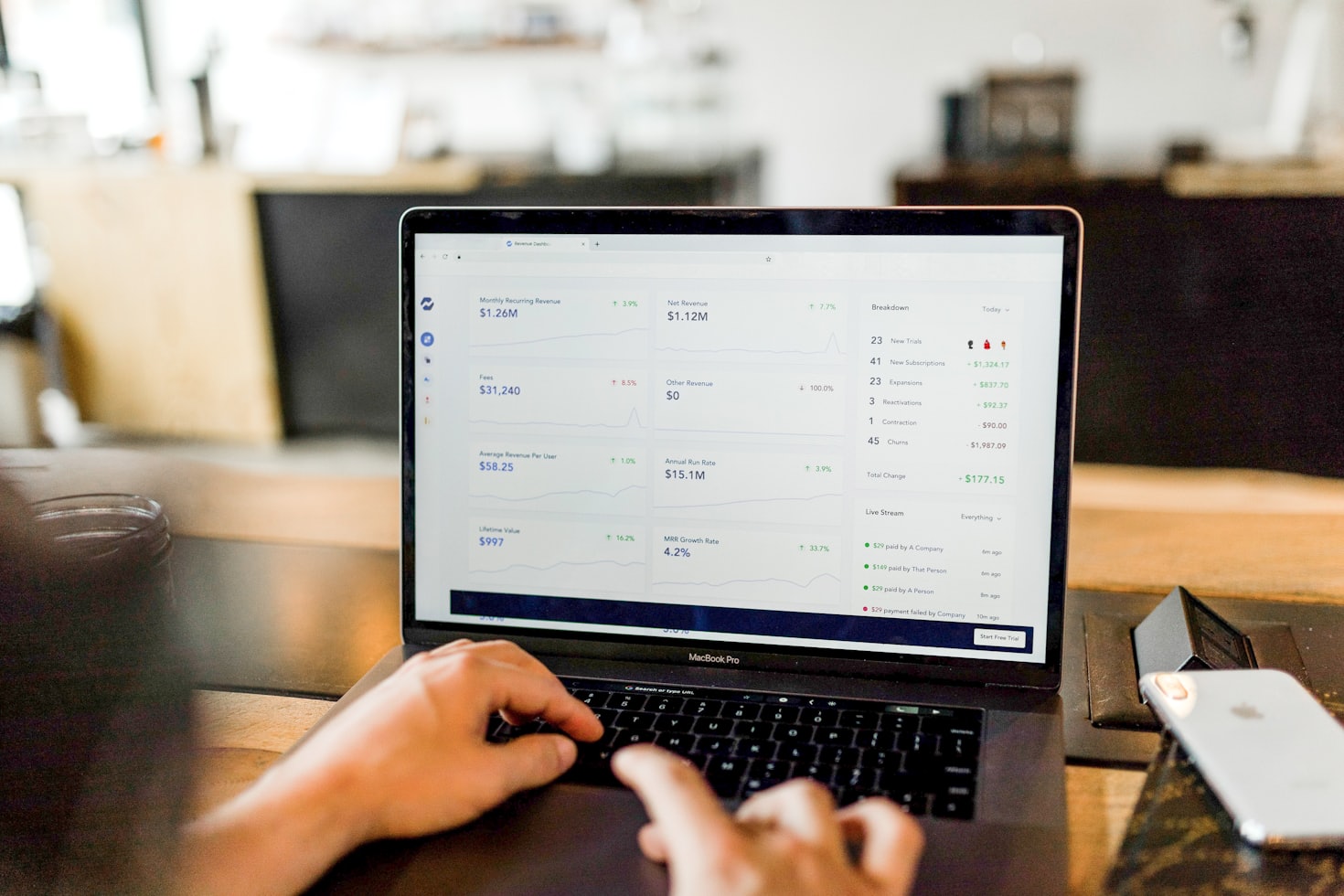
When Knowledge is Democratized A significant source of fear among intellectuals is the democratization of knowledge. Consider this: a five-year-old with an iPad and access to the internet now has more information at their fingertips than scholars of the past could access in a lifetime. Tools like ChatGPT, search engines, and online encyclopedias allow anyone to learn complex topics quickly and efficiently. For individuals who have dedicated years to mastering a craft or field of study, this can feel deeply unsettling.
Professors, lawyers, doctors, and artists are all grappling with the realization that AI can match, and in some cases exceed, their expertise. For example, AI-driven diagnostic tools in medicine can analyze symptoms and recommend treatments faster and more accurately than many doctors. Legal AI platforms can sift through vast amounts of case law in seconds, a task that would take human lawyers weeks.
This shift raises existential questions: What does it mean to be an expert when machines can replicate expertise? How can we measure human value in a world where intellect is no longer a uniquely human trait?
The New Frontier: Jobs of the Intellectual Revolution
As with the Industrial Revolution, the Intellectual Revolution will not only displace jobs but also create new ones. Understanding these new roles and their potential impact on humanity is crucial.
1. AI Trainers and Supervisors While AI can learn independently, it still requires human guidance. AI trainers are responsible for teaching machines how to interpret data correctly and refine their outputs. Supervisors ensure that AI systems operate effectively and align with practical goals.
2. Creative Collaborators Rather than replacing artists and writers, AI can augment their creativity. New roles will emerge for individuals who use AI as a tool to generate innovative ideas, designs, and narratives. For example, fashion designers might use AI to predict trends, while filmmakers could use it to create hyper-realistic visual effects.
3. Data Curators AI relies on vast amounts of data to function effectively. Data curators will be tasked with organizing, managing, and ensuring the quality of the information fed into AI systems. This will be a critical role in maintaining the accuracy and reliability of AI outputs.
4. AI Maintenance and Development Just as the Industrial Revolution created a need for mechanics and engineers, the Intellectual Revolution will require specialists to maintain and improve AI systems. This includes software engineers, data scientists, and machine learning specialists.
Societal Impact: New Opportunities and Challenges
The Intellectual Revolution offers immense potential to improve human life and create new opportunities. AI has the ability to solve complex problems, from accelerating medical research to improving infrastructure and making education more personalized. These advancements could lead to a higher standard of living and greater efficiency across industries.
At the same time, rapid advancements in AI bring challenges that demand attention. For instance, traditional roles in certain industries may change or disappear, requiring workers to adapt and acquire new skills. This shift will call for robust educational initiatives and innovative approaches to workforce development.
Preparing for the Future
To ensure that the Intellectual Revolution benefits all of humanity, proactive measures are needed. Governments, businesses, and individuals must work together to address the challenges posed by AI. Here are some steps we can take:
1. Invest in Education and Reskilling As traditional jobs are replaced, new skills will be in demand. Education systems must adapt to teach skills like critical thinking, creativity, and digital literacy. Lifelong learning initiatives will be essential to help workers transition into new roles.
2. Promote Ethical AI Development Ethics must be at the forefront of AI development. This includes creating regulations to prevent misuse, ensuring transparency in AI decision-making, and addressing issues of bias and discrimination.
3. Foster Collaboration Between Humans and AI Rather than viewing AI as a threat, we should embrace it as a partner. By leveraging AI’s capabilities, humans can achieve greater efficiency and innovation. For example, doctors can use AI to assist with diagnoses, allowing them to focus on patient care.
Conclusion
The Intellectual Revolution, driven by artificial intelligence, represents a turning point in human history. Like the Industrial Revolution before it, this era is characterized by both fear and opportunity. While AI challenges traditional notions of expertise and displaces certain jobs, it also creates new possibilities for innovation and progress. By embracing change, investing in education, and promoting ethical development, we can ensure that the benefits of this revolution are shared by all. The question is not whether the Intellectual Revolution will happen, but how we, as a society, will shape its course.
Brad Ballinger: Contact information available by request


Leave a Reply